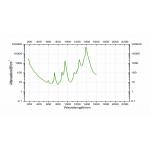
400 um Core/430um Fiber with hard plastic cladding ( Easy chemical
removal)
Fiberglass, or “glass fiber,” itself has a familiar base
structure and a wide variety of uses.
Fiberglass really is made of glass similar to that in windows or kitchen drinking glasses. To
manufacture fiberglass, glass is heated until molten,
then forced through superfine holes. This creates glass filaments
that are extremely thin—so thin, in fact, that they're best
measured in microns.
The glass would have to have a clear core surrounded by a
skin—called cladding,
and also made of glass—so that the cladding could reflect laser
light back into the core and keep it traveling along its path.
These flexible filament threads can be used in several
applications:
They can be woven into larger swatches of material or left in a
somewhat less structured form used for the more familiar puffy
texture used for insulation or soundproofing. The final application
is dependent on the length of the extruded strands (longer or
shorter) and the quality of the fiberglass.
For some applications, it's important that the glass fibers have
fewer impurities, however, this involves additional steps in the
manufacturing process.
The purity of the glass is maintained by using corrosion-resistant
plastic in the gas delivery system (valve blocks, pipes, seals) and
by precisely controlling the flow and composition of the mixture.
The process of making the preform blank is highly automated and
takes several hours. After the preform blank cools, it is tested for quality control
(index of refraction).
Specification :
| Item | Wavelength
Range | Hydroxyl
Content | Core
Diameter | Cladding
Diameter | Coating
Diameter | Core /
Cladding | Coating | Proof Test | Stripping
Tool |
| HCW050UGA | 250 - 1200 nm | High-OH | 50 μm ± 2% | 125 ± 1 μm | 250 μm ± 4% | Pure Silica /
Fluorine-Doped Silica | Acrylate | ≥100 kpsi | T08S13 |
| HCW050LGA | 400 - 2400 nm | Low-OH |
| HCW105UCA | 250 - 1200 nm | High-OH | 105 μm ± 2% | 125 ± 1 μm | 250 μm ± 4% | T08S13 |
| HCW105LCA | 400 - 2400 nm | Low-OH |
| HCW200UEA | 250 - 1200 nm | High-OH | 200 μm ± 2% | 220 ± 2 μm | 320 μm ± 5% | T10S13 |
| HCW200LEA | 400 - 2400 nm | Low-OH |